DBAddin
DBAddin is a ExcelDNA based Add-in for Database interoperability.
First, DBAddin provides DB Functions (see DBFuncs User-doc), which are an alternative to the Excel built-in MSQuery (integrated statically into worksheets having severe limitations in terms of querying and constructing parameterized queries (MS-Query allows parameterized queries only in simple queries that can be displayed graphically)).
Next, methods for working with database data (DBModifications: DBMapper, DBAction and DBSequences) are included. This also includes a row entry oriented way to modify data in so called DBSheets (see DBSheets).
DBAddin.NET is the successor to the VB6 based Office Database Addin, see also the slide-show for a quick overview.
Installation
- Dependencies/Prerequisites
- .NET 4.7 or higher (usually distributed with Windows)
- Excel (minimum 2007 because of Ribbons)
If any of these are missing, please install them yourself before starting DBAddin.
Download the latest zip package in https://github.com/rkapl123/DBAddin/tags, unzip to any location and run deployAddin.cmd in the folder Distribution. This copies DBAddin.xll, DBAddin.xll.config, DBAddinUser.config and DBAddinCentral.config to your %appdata%\Microsoft\AddIns folder and starts Excel for activating DBAddin (adding it to the registered Addins).
Settings
Settings can be configured in three config files, depending on your distribution requirements:
- DBAddin.xll.config in section appSettings. DBAddin.xll.config can have a reference
- to a DBAddinCentral.config (filename is free to define) in the file attribute of the appSettings element and
- to DBAddinUser.config (filename is free to define) in the configSource attribute of the UserSettings element
- DBAddin.xll.config is expected in the same folder as the DBAddin.xll (%appdata%\Microsoft\AddIns)
- DBAddinCentral.config (this is a reference copy of the appSettings section, where the key/value pairs override the settings in DBAddin.xll.config). This is meant to be a centrally maintained settings configuration.
- DBAddinUser.config (this is a reference copy of the UserSettings section, where the key/value pairs override both the settings in DBAddin.xll.config and DBAddinCentral.config). This is meant to be a user locally maintained settings configuration.
In the DBAddin settings Group, there is a drop-down named “settings”, where you can modify these three settings inside Excel.
After installation you’d want to adapt the connection strings (ConstConnStringN) that are globally applied if no function-specific connection string is given and environment N is selected. This can be done by modifying DBAddin.xll.config or the referred DBAddinUser.config or DBAddinCentral.config (in this example the settings apply to environment 3):
<appSettings>
<add key="ConfigName3" value="MSSQL"/>
<add key="ConstConnString3" value="provider=SQLOLEDB;Server=Lenovo-PC;Trusted_Connection=Yes;Database=pubs;Packet Size=32767"/>
<add key="ConfigStoreFolder3" value="C:\dev\DBAddin.NET\source\ConfigStore"/>
<add key="ConnStringSearch3" value="provider=SQLOLEDB"/>
<add key="ConnStringReplace3" value="driver=SQL SERVER"/>
<add key="dbGetAll3" value="sp_helpdb"/>
<add key="dbGetAllFieldName3" value="name"/>
<add key="DBidentifierCCS3" value="Database="/>
<add key="dbPwdSpec3" value="PWD="/>
<add key="DBSheetConnString3" value="DRIVER=SQL SERVER;Server=Lenovo-PC;UID=sa;PWD=;Database=pubs;"/>
<add key="DBSheetDefinitions3" value="C:\dev\DBAddin.NET\definitions"/>
<add key="ownerQualifier3" value=".dbo."/>
</appSettings>
Explanation:
ConfigNameN: freely definable name for your environment (e.g. Production or your database instance)ConstConnStringN: the standard connection string used to connect to the database. SetODBC;in front to specify ODBC connection strings explicitly.ConfigStoreFolderN: all config files (*.xcl) under this folder are shown in a hierarchical manner in “load config”ConnStringSearchN: part to be searched for replacement within the standard connection string in DBModifiers and DBRowFetch.ConnStringReplaceN: replacement for abovedbGetAllN: command for retrieving all databases/schemas from the database can be entered (for MS SQL server this is “sp_helpdb” for Oracle its “select username from sys.all_users”.dbGetAllFieldNameN: If the result of above command has more than one column (like in sqlserver), you have to give the field name where the databases can be retrieved from.DBidentifierCCSN: used to identify the database within the standard connection string or within DBSheetConnStringdbPwdSpecN: Password entry specifier within DBSheetConnStringDBSheetConnStringN: the connection string used to connect to the database for DBSheet definitions. If this is not set the standard connection stringConstConnStringN is used.DBSheetDefinitionsN: path to the stored DBSheetdefinitions (default directory of assign DBsheet definitions and load/save DBSheet Definitions)ownerQualifierN: default owner qualifier for table when loading DBSheet definitions, if table name is not fully qualified (legacy DBSheet definitions)
Other Settings
Other (general) settings possible in DBAddin.xll.config (or DBAddinCentral.config/DBAddinUser.config):
<add key="CmdTimeout" value="30" />
<add key="CnnTimeout" value="15" />
<add key="ConfigSelect" value="SELECT TOP 10 * FROM !Table!" />
<add key="ConfigSelectWithCount" value="SELECT (SELECT Count(*) FROM !Table!) Anzahl, TOP 10 * FROM !Table!" />
<add key="ConfigSelect2" value="SELECT * FROM !Table!" />
<add key="ConfigSelectPreference" value="WithCount" />
<add key="connIDPrefixDBtype" value="MSSQL" />
<add key="DBMapperCUDFlagStyle" value="TableStyleLight11" />
<add key="DBMapperStandardStyle" value="TableStyleLight9" />
<add key="DBSheetAutoname" value="True" />
<add key="DebugAddin" value="False" />
<add key="DefaultDBDateFormatting" value="0" />
<add key="DefaultEnvironment" value="3" />
<add key="disableSettingsDisplay" value="addin"/>
<add key="DMLStatementsAllowed" value="True" />
<add key="DontChangeEnvironment" value="False" />
<add key="ExcelVersionForPivot" value="7" />
<add key="legacyFunctionMsg" value="True" />
<add key="LocalHelp" value="C:\dev\DBAddin.NET\docs\doc\rkapl123.github.io\DBAddin\index.html"/>
<add key="localUpdateFolder" value="" />
<add key="localUpdateMessage" value="New version available in local update folder, start deployAddin.cmd to install it:" />
<add key="maxNumberMassChange" value="10" />
<add key="repairLegacyFunctionsAutoOpen" value="True" />
<add key="shortCutRefreshData" value="^R" />
<add key="shortCutJumpButton" value="^J" />
<add key="shortCutDeleteRow" value="^D" />
<add key="shortCutInsertRow" value="^I" />
<add key="updatesDownloadFolder" value="C:\temp\" />
<add key="updatesMajorVersion" value="1.0.0." />
<add key="updatesUrlBase" value="https://github.com/rkapl123/DBAddin/archive/refs/tags/" />
Explanation:
CmdTimeout: the default timeout for a command to execute.CnnTimeout: the default timeout for connecting.ConfigSelectPostfix: Use this template instead of standard config (currentlySELECT TOP 10000 * FROM <Table>) when inserting cell configurations. The respective Table is being replaced into!Table!. Add Postfix to make different choices, the preferred choice is given in next setting.ConfigSelectPreference: select the preferred choice if ConfigSelect here by setting Postfix as value. IfConfigSelectPostfix is not found in the choices, the plainConfigSelectis taken. If that is also not found, no template is used and the standard config is taken.connIDPrefixDBtype: legacy DBSheet definitions have a Prefix inconnIDbefore the database that needs to be removed, this is the String to remove …DBMapperCUDFlagStyle: Style for setting Excel data tables when having CUD Flags set on DBMappers.DBMapperStandardStyle: Style for setting Excel data tables when not having CUD Flags set on DBMappers.DBSheetAutoname: When inserting DBSheet Definitions, automatically name Worksheet to the table name, if this is set.DebugAddin: activate Info messages to debug addin.DefaultDBDateFormatting: default formatting choice for DBDate.DefaultEnvironment: default selected environment on startup.disableSettingsDisplay: enter a name here for settings that should not be available for viewing/editing to the user (addin: DBAddin.xll.config,central: DBAddinCentral.config,user: DBAddinUser.config).DMLStatementsAllowed: Allows DML Statements in the Ad-hoc SQL Query Tool.DontChangeEnvironment: prevent changing the environment selector (Non-Production environments might confuse some people or lead to errors).ExcelVersionForPivot: The default Version when creating DBSetQuery enabled pivot tables (see DBFuncs User-doc, 0=2000, 1=2002, 2=2003, 3=2007, 4=2010, 5=2013, 6=2016, 7=2019).legacyFunctionMsg: Alternative Message for replacing legacy functions (different language).LocalHelp: the path to local help files down-loadable here. To include it, extract the package into the respective folder and assign the file accordingly.localUpdateFolder: For updating the DB-Addin Version, you can provide an alternative folder, where the deploy script and the files are maintained for other users.localUpdateMessage: For the alternative folder update, you can also provide an alternative message to display.maxNumberMassChange: Threshold of Number of changes in CUDFlag DBMappers to issue a warning.repairLegacyFunctionsAutoOpen: Set this to False if legacy DB Addin functions should not be checked/repaired on auto open of workbooks.shortCutRefreshData: Set this to override the default value of the refreshData context button and avoid conflicts with other addins. For syntax see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/office/ff197461.aspx.shortCutJumpButton: Set this to override the default value of the jump to DBFunc/target context button and avoid conflicts with other addins.shortCutDeleteRow: Set this to override the default value of the delete Row context button and avoid conflicts with other addins.shortCutInsertRow: Set this to override the default value of the insert Row context button and avoid conflicts with other addins.updatesDownloadFolder: You can specify a different download folder here instead ofC:\temp\.updatesMajorVersion: Usually the versions are numbered 1.0.0.x, in case this is different, the Major Version can be overridden here.updatesUrlBase: Here, the URL base for the update zip packages can be overridden.
To change the settings, use the drop-down “settings” where you can modify the DBAddin.xll.config and the referred DBAddinCentral.config including XML validation. If you have multiple same named entries in your settings files, the last one is taken as the active setting. The settings dialog has a drop-down at its bottom providing all the available settings to be selected. On selection, the chosen setting is added to the bottom of the current open config. For + env settings, an input box will provide the possibility to set the number to be used instead of + env. There are other specific settings available for use with DB Functions, DB Modifications and DB Sheets, see there for more details.
Environment, About Box, Settings, Log and fix legacy functions
The environment drop-down selector on top of the DBAddin settings Group allows to choose the environments defined with the ConfigNameN settings (and the associated data). If this drop-down is disabled, you can enable it by setting DontChangeEnvironmentto false`.
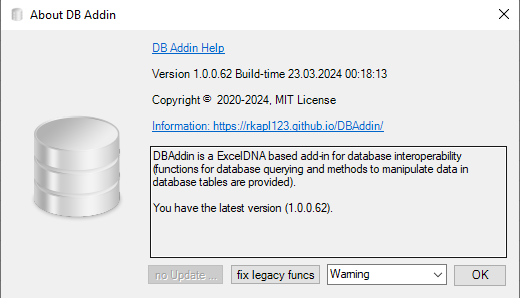
About Box and updates
The About Box can be reached by clicking the small dialogBox Launcher in the right bottom corner of the DB Addin settings group of the DBAddin Ribbon:
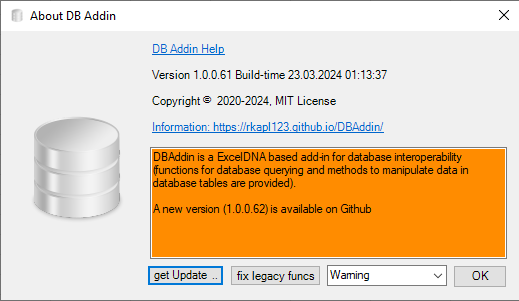
You can get updates from here, in case there are new versions, this is shown with an orange background and a hint:
There is a possibility to set the future log events displayed (the starting value is set in the config file). You can also fix functions from the legacy DBAddin (VB6) using the “fix legacy funcs” button in case you decided to skip the possibility offered on opening a Workbook.
Log
To see the Log, there is a separate Button in the settings group of the DBAddin ribbon that also indicates the existence of warning log entries with a red exclamation mark.
Settings
In the DBAddin settings Group, there is a drop-down “settings”, where you can modify the DBAddin.xll.config and the referred DBAddinUser.config and DBAddinCentral.config including XML validation.
At the bottom of all settings dialogs, there is a drop-down showing the available settings. Those settings that are environment-dependent (ConfigNameN) are automatically displayed with the current selected environment number after the name. If you select the setting, it will be added at the bottom of all settings, you can cut/paste it anywhere you want. If the setting is already existing, an error message is displayed and the existing setting is highlighted. Any XML validation errors display the location with a row and column number, however these refer to the flat version of the text (without any word-wrap).
Custom workbook properties
Right besides the settings drop-down, there is a shortcut button to the Workbook properties (being the standard dialog Advanced Properties, accessible via File/Info) that allows you to change custom properties settings for DBAddin. A green check on that button shows that the custom property DBFskip is not set to true for this workbook, therefore DB functions are always refreshed on opening the workbook.
Tools
Besides the hierarchical menu “DBConfigs” (see DBFuncs User-doc) and the DBSheet Configuration (see DBSheets) there are other tools in the DB Addin Tools group:
Purge
The DBListFetch’s and DBRowFetch’s target areas’ extent is stored in hidden named ranges assigned both to the calling function cell (DBFsource(Key)) and the target (DBFtarget(Key)). These hidden names are used to keep track of the previous content to prevent overwriting, clearing old values, etc. Sometimes during copying and pasting DB Functions, these names can get mixed up, leading to strange results or non-functioning of the “jump” function. In these cases, there is a tool in the DB Addin tools group, which may be used to “purge” these hidden named ranges in case of any strange behaviour due to multiple name assignments to the same area. This button is only usable if clicked while pressing the Shift button. If the purge button is clicked while pressing the Ctrl Button, the hidden names used for the DB functions are unhidden and the Name manager is displayed.
Buttons
The button “Buttons” is used for switching design mode for DBModifier Buttons (identical to standard Excel button “Design Mode” in Ribbon “Developer tab”, Group “Controls”)
AdHocSQL Tool
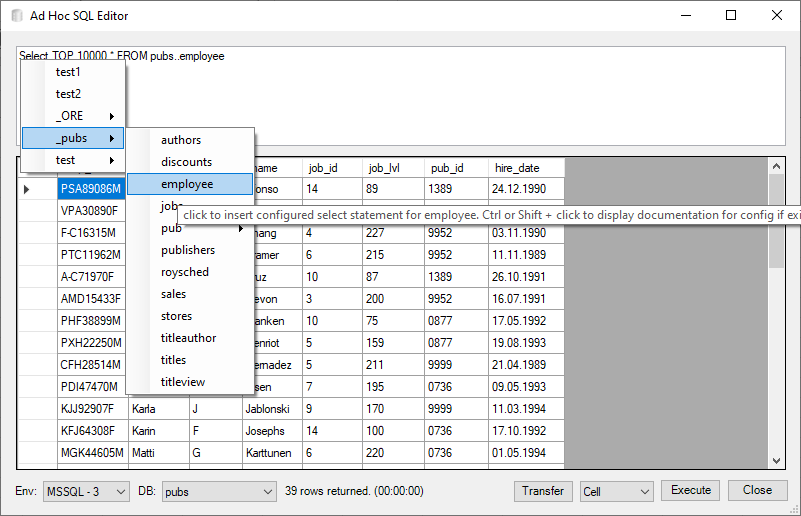
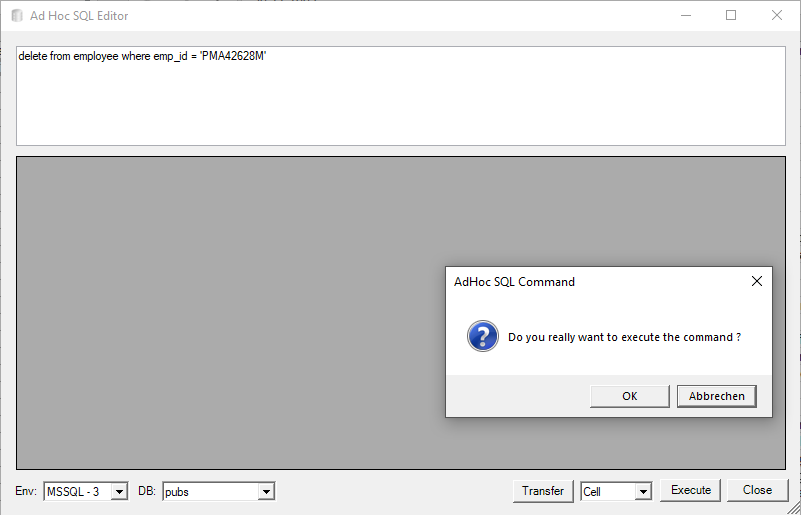
Another tool is the entry of quick (ad hoc) SQL Commands in the combo box below the settings drop-down. Changing the combo box or clicking the dialog box launcher below it, opens the AdHoc SQL Command dialog:
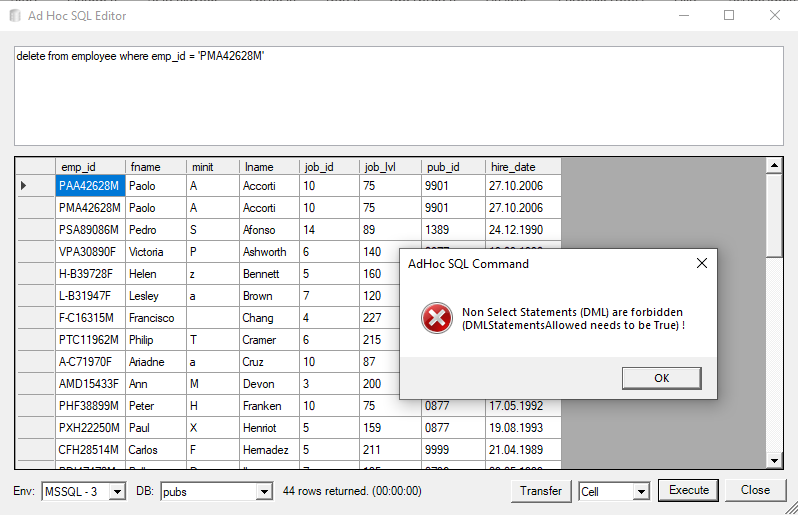
Select Statements (beginning with select) are executed immediately, empty statements (using a space character in the combo-box) don’t execute anything, and everything else is regarded as a DML command and is only executed after confirmation:
For safety reasons, the DML commands an blocked until an additional setting <add key="DMLStatementsAllowed" value="True" /> is being set. This is indicated by an error message:
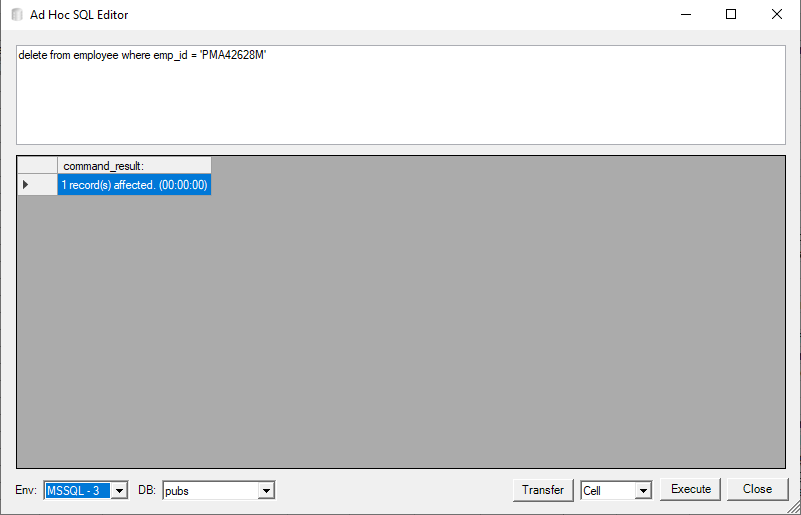
Results are shown below the SQL Command text entry, for row returning commands, the rows returned are shown including the time it took to finish the command at the bottom of the dialog. In case of an error the exception from the database command is displayed, for DML commands the records affected are shown (again including the time it took to finish the command):
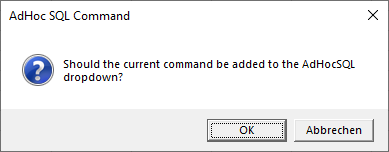
You can modify the command in the AdHoc SQL Command dialog. By clicking Execute or pressing Ctrl-Return the command will be executed. To change the database context, use the drop-down DB:. To change the environment (connection string), use the drop-down Env:. To leave the dialog, hit ESC or click Close, in case the SQL command has changed, you will be prompted whether to add the new command to the combo-box:
To transfer the SQL command into the current cell, click Transfer or press Shift-Return. Depending on the type selected in the drop-down besides the Transfer button this will either
- for
Cell: put the command into an empty cell, in case there is a DB Function there, replacing any query inside that function (this obviously only makes sense for select statements). - for
ListFetch: create aDBListFetchfunction in the current cell and put the command into the functions query (this obviously only makes sense for select statements). - for
RowFetch: create aDBRowFetchfunction in the current cell and put the command into the functions query (this obviously only makes sense for select statements). - for
ListObject: create aDBSetQueryfunction (targeted to a new ListObject) in the current cell and put the command into the functions query (this obviously only makes sense for select statements). - for
Pivot: create aDBSetQueryfunction (targeted to a new Pivot Table) in the current cell and put the command into the functions query (this obviously only makes sense for select statements).
You can always interrupt long running commands by clicking Close (or hitting ESC) or Transfer. A question whether to cancel the interruption is provided then.
Issued commands are stored in the drop-down and persisted in the user settings after prompting the user, being reloaded at start-up of the Add-In (Excel).
If you want to remove them, open the User-Settings as described in Settings and remove all unwanted entries starting with key="AdhocSQLcmd.."
Also the chosen environment and the database context is stored along with each command (subsequent changes to the environment and database are stored without prompting), the transfer type is stored apart from that.
If the general DB-Addin environment is different from the stored environment of the command, a warning/question is displayed that allows to reset the environment to the general environment. If this is done, any changes to the environment and the database are not stored after closing the AdHocSQL Tool.
Building
All packages necessary for building are contained, simply open DBaddin.sln and build the solution. The script deployForTest.cmd can be used to quickly deploy the built xll and configurations to %appdata%\Microsoft\AddIns after choosing the solution configuration (Release or Debug).
Testing
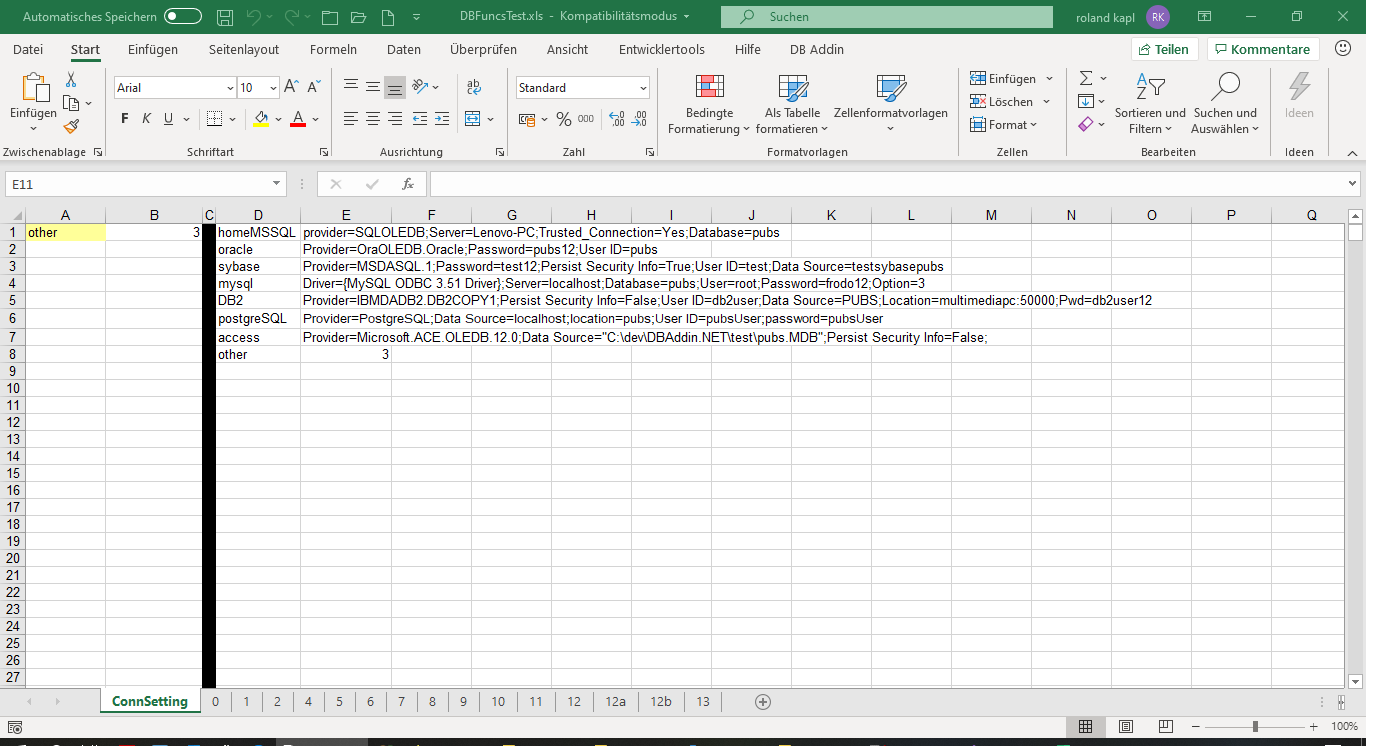
Testing for MS SQL Server and other databases (MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, DB2, Sybase and Access) can be done using the Testing Workbook “DBFuncsTest.xls”. To use that Testing Workbook you’ll need the pubs database, where I have scripts available for Oracle, Sybase, DB2, PostgreSQL and MySql here (the MS-SQLserver version can be downloaded here). I’ve also added a pubs.mdb Access database in the test folder.
When starting the Testworkbook, after waiting for the – probable – connection error, you have to change the connection string(s) to suit your needs (see below for explanations).
Several connection strings for “DBFuncsTest.xls” are placed to the right of the black line, the actual connection is then selected by choosing the appropriate short-name (drop-down) in the yellow input field. After the connection has been changed don’t forget to refresh the queries/DBforms by right clicking and selecting “refresh data”.
Road map
Following topics are still to be done:
- Utilizing optimistic concurrency for DBSheets (similar to the old Addin, but with ADO.NET support)
History (from the very beginning)
- 2006: First versions of DBFuncs and DBSheets implemented as xla Addins.
- 31/01/2007: Published as a Codeproject article
- 02/11/2007: Changed implementation to VB 6.0 and made this available at sourceforge
- 01/04/2019 - 24/11/2020: Changed implementation to ExcelDNA based and moved to Github.