DBModifications
DBModifications can be used to
- save Excel Range data to database table(s): DBMapper
- modify DB Data using Data Manipulation SQL (update, delete, etc.): DBAction
- and creating sequences of these activities: DBSequence.
The target data referred to by DBMapper and DBAction (data is the DML SQL statement(s)) is specified by special Range names, any other definitions (environment, target database, etc.) is stored in a custom property of the workbook having the same name as the target range.
Examples for the usage of DBMapper can be found in the DBMapperTests.xlsx Workbook.
Create DBModifiers
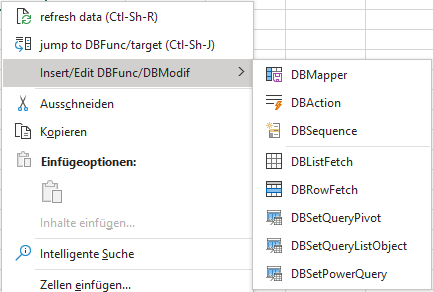
You can create the three DB Modifiers by using the cell context menu:
The DBModifier creation/editing is shown below (examples already filled, when activated on a blank cell all entries are empty):
(some features cannot be set in the dialogs, e.g. a customized confirmation text for the “Ask for execution” dialog, this is done with Edit DBModifier Definitions, see below)
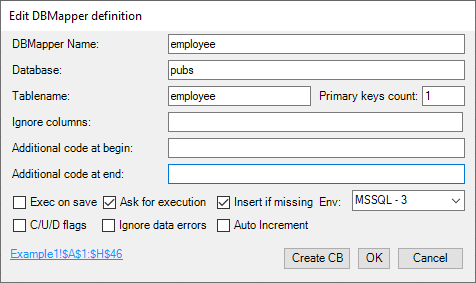
DB Mappers are created/edited with the following dialog:
- DBMapper Name: Enter the name for the selected Range (containing the Data including header fields) that will be used to identify the DBMap in the “Execute DBModifier” Group dropdowns. If no name is given here, then UnnamedDBMapper will be used to identify it.
- Tablename: Database Table, where Data is to be stored.
- Primary keys count: amount of columns from the left to be used as primary keys for updating table data. Enter 0 here for special “insert-only” Mappers (all entries are added to a table that doesn’t need to have primary columns), recommended to be used with deleteBeforeMapperInsert (removes all content of the table before inserting)
- Database: Database to store DBMaps Data into.
- Ignore Columns: comma separated list of field names to be ignored (e.g. helper columns or irrelevant columns).
- Additional Code at begin: additional code (e.g. stored procedure) to be executed before DBMapper execution.
- Additional Code at end: additional code (e.g. stored procedure) to be executed after DBMapper execution.
- Insert If Missing: if set, then insert row into table if the primary key is missing there. Default = False (only update, an error is thrown if the record couldn’t be found).
- Store DBMap on Save: should DBMap also be saved on Excel Workbook Saving? (default no). If multiple DBModifiers (DB Mappers and DB Actions, DB Sequences are not bound to a worksheet) are defined to be stored/executed on save, then the DBModifiers being on the active worksheet are done first (without any specific order), then those on the other worksheets are done (also without any specific order).
- Env: The Environment, where connection id should be taken from (if not existing, take from selected Environment in DB Add-in General Settings Group).
- Exec on Save: Should the DBMap be executed when the workbook is being saved?
- Ask for execution: Before execution of the DBMap, ask for confirmation. A custom text can be given in the CustomXML definition element confirmText (see below).
- C/U/D Flags: special mode used for row-by-row editing (inserting, updating and deleting rows). Only edited rows will be done when executing. Deleting rows is done with the special context menu item “delete Row” (or pressing Ctrl-Shift-D). This mode is the basis for DBSheets, a specific usage of DBMappers.
- Ignore data errors: replace excel errors like #VALUE! with null on updating/inserting. Otherwise an error message is passed and execution is skipped for that row.
- Auto Increment: Allow empty primary column values (only for a single primary key!) in use with tables that have the IsAutoIncrement property set for this primary column (typically because of an identity specification for that column in the Database).
- Create CB: create a command-button for the DB Sequence in the current Worksheet.
- Hyperlink: click on it to highlight/select the DB Mapper area.
You can always edit these parameters by selecting a cell in the DB Mapper area and invoking the context menu again.
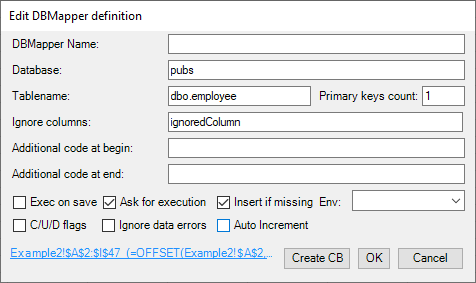
The range underlying the name that is used for holding the data to be stored can be constructed in three different ways:
- A plain address: Here the range is automatically extended by using the first column and the first row (header row), if no Auto Increment or C/U/D Flags are set. In such a case, empty primary column(s) are allowed, so the automatic extension of rows is not done.
- A named offset formula (that is used to dynamically assign the data range).
- A data list object (especially in use for C/U/D Flags).
The clickable Hyperlink shows the range address of the data range, a named offset formula is displayed after the address:
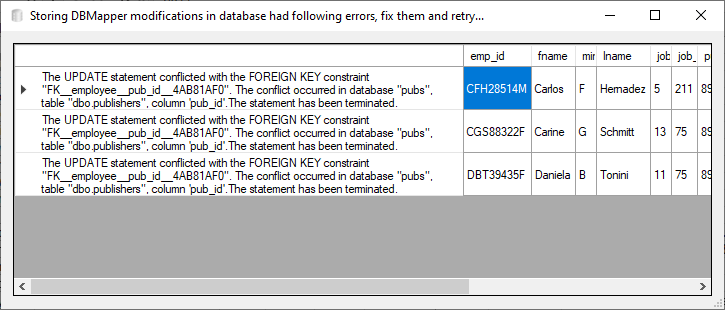
When storing data to the database, field specific restrictions (date type, length) are checked immediately by the .NET DataAdapter, everything else (all constraints, especially foreign keys) is checked on invoking update at the end of filling the DataAdapter. Any occurred errors are presented in a data grid:
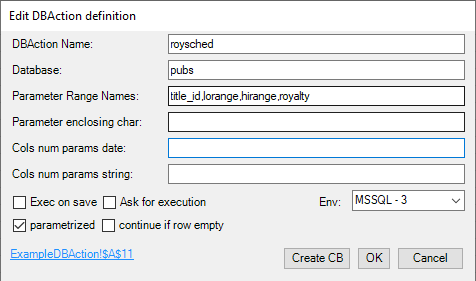
DB Actions are created/edited with following dialog:
- DBAction Name: Enter the name for the selected cell or range that will be used to identify the DBAction in the “Execute DBModifier” Group dropdowns. If no name is given here, then UnnamedDBAction will be used to identify it.
- Database: Database to do the DBAction in.
- Parameter Range Names: string of named ranges (if necessary qualified with sheet name!range_name) to be used as parameters that are replaced into the template string, where the order of the parameter range determines which placeholder is being replaced
- Cols num params date: comma separated locations of numerical parameters that should be converted as date values (using the default DBDate formatting), if a cell value can be evaluated as numeric.
- Cols num params string: comma separated locations of numerical parameters that should be converted as strings, if a cell value can be evaluated as numeric.
- Exec on Save: Should the DBAction be executed when the workbook is being saved?
- Ask for execution: Before execution of the DBAction, ask for confirmation. A custom text can be given in the CustomXML definition element confirmText (see below).
- Env: The Environment, where connection id should be taken from (if not existing, it is taken from selected Environment in DB Add-in General Settings Group).
- parametrized: If checked, brings parameters into the template paramString by replacing the placeholders (enclosed by ! if not overridden in paramEnclosing) with the values in the corresponding paramRanges.
- continue if row empty: if all values in the given Ranges are empty (or errors) for a row, continue by skipping the row (otherwise processing stops at this row), defaults to false
- The actual DBAction to be done is defined in a range that is named like the DBAction definition (the hyperlink takes you there). This range can be dynamically computed as all ranges in excel.
- Hyperlink: click on it to highlight/select the DB Action range.
- Create CB: create a command-button for the DB Sequence in the current Worksheet.
Example for parametrization: DB Action cell contains INSERT INTO Test (Col1,Col2,Col3,Col4) VALUES(!1!,!2!,!3!,!4!); Cols num params string: 1; Cols num params date: 3; Parameter Range Names: paramC1,paramD1,paramE1,paramF1
Where cells in parameter range paramC1, paramD1, paramE1 and paramF1 contain the parameters being replaced into the template string. The first range is being replaced into !1!, the second in !2!, and so on. Parameter ranges are read row-wise from left to right (as usual) and need to have the same size.
Assuming parameter range paramC1, paramD1 and paramE1 contain numbers, the parameters in paramC1 are replaced in the template as strings (surrounded by quotes), parameters in paramD1 are unquoted numbers and parameters in paramE1 are replaced in the template as date values (using the default DBDate formatting).
Date values (formatted as dates) are automatically recognized, there is no need to explicitly mark them with Cols num params date
You can always edit these parameters by selecting a cell in the range of the DB Action area and invoking the context menu again.
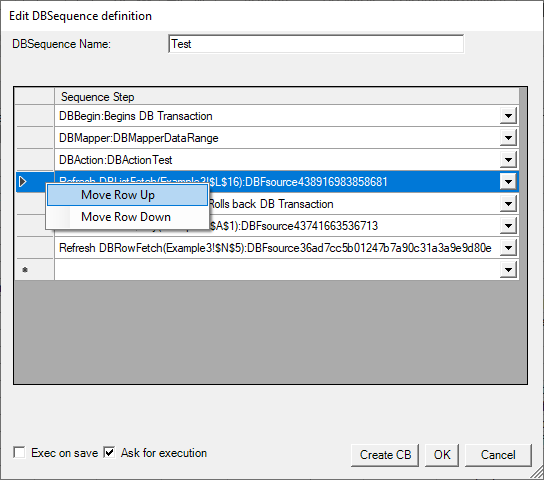
DB Sequences are created/edited with following dialog:
- DBSequence Name: Enter the name for the selected Range that will be used to identify the DBSequence in the “Execute DBModifier” Group dropdowns. If no name is given here, then UnnamedDBAction will be used to identify it.
- Exec on Save: Should the DBSequence be executed when the workbook is being saved?
- Ask for execution: Before execution of the DBSequence, ask for confirmation. A custom text can be given in the CustomXML definition element confirmText (see below).
- Sequence Step Data-grid: here the available DBMappers, DBActions and DBFunctions (DBListfetch/DBRowFetch/DBSetQuery) can be added that are then executed in Sequence. If you are executing all sequence steps in the same environment, its possible to run the sequence in a transaction context by placing DBBegin at the top and DBCommitRollback at the bottom of the sequence.
- move the sequence steps up and down by selecting a row and using the context menu (right mouse button).
- Create CB: create a command-button for the DB Sequence in the current Worksheet.
As DB Sequences have no Range with data/definitions, invoking the context menu always creates new DB Sequences. You can edit existing DB Sequences by Ctrl-Shift clicking the Execute DBModifier Groups dropdown menus or by Ctrl-Shift clicking the created command-buttons.
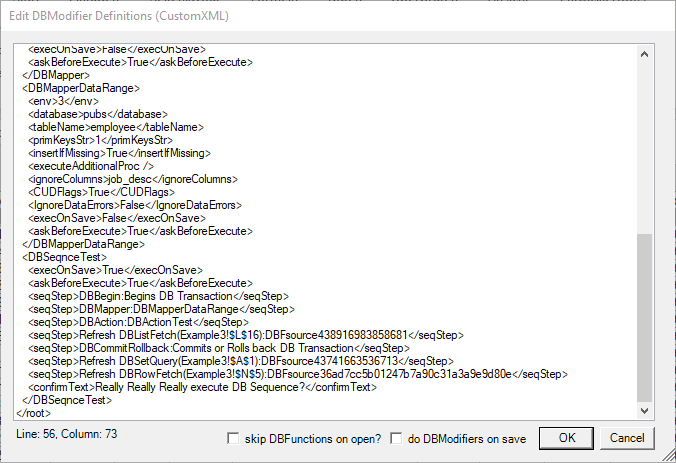
Edit DBModifier Definitions
All DBModifier definitions (done in XML) can be viewed by clicking the dialogBox Launcher on the right bottom corner of the Execute DBModifier Ribbon Group
together with Ctrl and Shift. This opens the Edit DBModifier Definitions Window:
Here you can edit the definitions directly and also insert hidden features like the customized confirmation text in the element confirmText.
The DBModifiers can be executed either
… using the Execute DBModifier Groups dropdown menus..
… or using command-buttons that were generated with the creation dialogs (the name of the control box has to be the same as the DBModifier definition/DBModifier Range)..
… or be done on saving the Workbook.
… or by issuing the VBA command result = Application.Run("executeDBModif", <DBModifierName>, <headlessFlag>), where <DBModifierName> is the name of the DB Modifier including the type (so DBMapperemployee or DBActionpublishersDelete) and <headlessFlag> is a boolean flag indicating whether any user-interaction (as controllable by the Add-in) should be avoided, all errors collected in nonInteractiveErrMsgs and returned in the result of the call.
You can edit the DBModifiers either by Ctrl-Shift clicking the Execute DBModifier Groups dropdown menus..
.. or by Ctrl-Shift clicking the created command-buttons.
.. or by using the Insert/Edit DBFunc/DBModif context menu within a DBMapper or DBAction range.
Additional macro functions available for setting/accessing settings
By issuing the VBA command Application.Run("setExecutionParam", Param, Value), where Param is the name of the parameter and Value is the value it should be set to, following settings can be set via VBA:
- headLess: sets nonInteractive to True or False
- selectedEnvironment: sets SettingsTools.selectedEnvironment to the value passed (zero based environment: 0 is the first, 1 the second, etc.)
- ConstConnString: sets SettingsTools.ConstConnString to the value passed
- CnnTimeout: sets SettingsTools.CnnTimeout to the value passed
- CmdTimeout: sets SettingsTools.CmdTimeout to the value passed
- preventRefreshFlag: sets Functions.preventRefreshFlag to the value passed (True: prevents refreshing of all DB Functions, False: enables refreshing again. Also see DB Functions refresh prevention in Main DBAddin Doc)
By issuing the VBA command result = Application.Run("getExecutionParam", Param), where Param is the name of the parameter the current settings of the following parameters are returned:
- selectedEnvironment: returns SettingsTools.selectedEnvironment (zero based environment: 0 is the first, 1 the second, etc.)
- env() : returns the selected environment (1 is the first, 2 the second, etc.)
- ConstConnString: returns SettingsTools.ConstConnString
- CnnTimeout: returns SettingsTools.CnnTimeout
- CmdTimeout: returns SettingsTools.CmdTimeout
- preventRefreshFlag: returns Functions.preventRefreshFlag
- nonInteractiveErrMsgs: returns the currently collected error messages
- … and any other key being set in the DBAddin settings (DBAddin.xll.config, DBAddinCentral.config or DBaddinUser.config)
Additional settings (“hidden” as they are not available in creation dialogs)
Following Settings of DBModifiers can only be edited in the Edit DBModifier Definitions Window:
confirmText(all DB Modifiers, String): an alternative text displayed in the confirmation of DB Modifiers.avoidFill(only DBMappers, Boolean): prevent filling of whole table during execution of DB Mappers, this is useful for very large tables that are incrementally filled and would take unnecessary long time to start the DB Mapper. If set to true then each record is searched independently by going to the database. If the records to be stored are not too many, then this is more efficient than loading a very large table.deleteBeforeMapperInsert(only DBMappers, Boolean): removes all content of the table before inserting the contents again.onlyRefreshTheseDBSheetLookups(only DBMappers, String): contains a list of addresses of DBListfetch function cells in the DBSheetLookups sheet that exclusively should be refreshed after the corresponding DBSheet was saved. If empty, all lookups are refreshed when the DBSheet was saved. Always provide a comma BEFORE the cell address (e.g.<onlyRefreshTheseDBSheetLookups>,Q1,S1</onlyRefreshTheseDBSheetLookups>to prevent refreshing of all lookups (DBListfetch functions) in sheet DBSheetLookups, except those in cell Q1 and S1)!preventColResize(only DBMappers, Boolean): prevent automatic resizing of DB Mappers columns to include new ones, this is useful if header columns can be added accidentally and thus lead to errors.preventAutoInc(only DBMappers, Boolean): prevent autoincrement functionality for tables that have autoincrementing primary keys. To be used together withset IDENTITY_INSERT <tablename> ONin “Additional Code at begin” in order to directly insert primary keys into an identity field.
Settings
Following Settings in DBAddin.xll.config or the referred DBAddinCentral.config or DBaddinUser.config affect the behaviour of DBModifiers:
<add key="CmdTimeout" value="30" />
<add key="CnnTimeout" value="15" />
<add key="DefaultEnvironment" value="3" />
<add key="DontChangeEnvironment" value="False" />
<add key="DBMapperCUDFlagStyle" value="TableStyleLight11" />
<add key="DBMapperStandardStyle" value="TableStyleLight9" />
<add key="DebugAddin" value="False" />
<add key="maxNumberMassChange" value="10" />
<add key="connIDPrefixDBtype" value="MSSQL" />
<add key="DBSheetAutoname" value="True" />
Explanation:
CmdTimeout: the default timeout for a command to execute.CnnTimeout: the default timeout for connecting.DefaultEnvironment: default selected environment on start-up.DontChangeEnvironment: prevent changing the environment selector (Non-Production environments might confuse some people).DBMapperCUDFlagStyle: Style for setting Excel data tables when having CUD Flags set on DBMappers (to find the correct name for this enter? ActiveCell.ListObject.TableStylein the VBE direct window having selected a cell in the desirably formatted data table).DBMapperStandardStyle: Style for setting Excel data tables when not having CUD Flags set on DBMappers.DebugAddin: activate Info messages to debug add-in.maxNumberMassChange: Threshold of Number of changes in CUDFlag DBMappers to issue a warning.connIDPrefixDBtype: Sometimes, legacy DBSheet definitions have a Prefix, this is the prefix to remove.DBSheetAutoname: When inserting DBSheet Definitions, automatically name Worksheet to the table name, if this is set.