Script Addin provides an easy way to define and run script interactions started from Excel.
Using ScriptAddin
Running an script is simply done by selecting the desired executable (R, Python, Perl, whatever was defined) on the dropdown “ScriptExecutable” in the Script Addin Ribbon Tab and clicking “run
When running scripts, following is executed:
- The input arguments (arg, see below) are written to files,
- (optional, if defined) the scripts defined inside Excel are written,
- defined/written scripts are called using the executable located in ExePath/exec (see settings) and
- the defined results/diagrams that were written to files are read and placed in Excel.
When holding the Ctrl-Key pressed while clicking “run
When holding the Shift-Key pressed while clicking “run
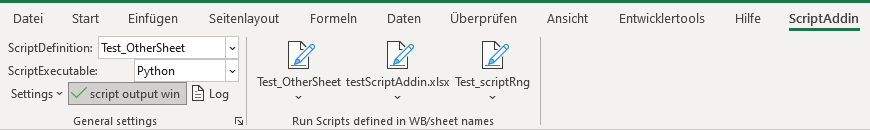
Defining ScriptAddin script interactions (ScriptDefinitions)
script interactions (ScriptDefinitions) are defined using a 3 column named range (1st col: definition type, 2nd: definition value, 3rd: (optional) definition path):
The Scriptdefinition range name must start with “Script_” (or “R_Addin” as a legacy compatibility with the old R Addin) and can have a postfix as an additional definition name. If there is no postfix after “Script_”, the script is called “MainScript” in the Workbook/Worksheet.
A range name can be at Workbook level or worksheet level. In the ScriptDefinition dropdowns the worksheet name (for worksheet level names) or the workbook name (for workbook level names) is prepended to the additional postfixed definition name.
So for the 8 definitions (range names) currently defined in the test workbook testRAddin.xlsx, there should be 8 entries in the Scriptdefinition dropdown:
- testScriptAddin.xlsx, (Workbooklevel name, runs as MainScript)
- testScriptAddin.xlsxAnotherDef (Workbooklevel name),
- testScriptAddin.xlsxErrorInDef (Workbooklevel name),
- testScriptAddin.xlsxNewResDiagDir (Workbooklevel name),
- Test_OtherSheet, (name in Test_OtherSheet)
- Test_OtherSheetAnotherDef (name in Test_OtherSheet),
- Test_scriptRngScriptCell (Test_scriptRng) and
- Test_scriptRngScriptRange (Test_scriptRng)
In the 1st column of the Scriptdefinition range are the definition types, possible types are
type: the script type to be used.exec(orrexecas a legacy compatibility with the old R Addin): an executable, being able to run the script in line “script”. This is only needed for overriding theExePath<ScriptType>in the AppSettings in the ScriptAddin.xll.config file.path: path to folders with dlls/executables (semicolon separated), in case you need to add them. Only needed when overriding thePathAdd<ScriptType>in the AppSettings in the ScriptAddin.xll.config file.envvar: environment variables to add to the process (each line will be one variable/value entry). Only needed when overridingEnvironVarName<ScriptType>/EnvironVarValue<ScriptType>settings in the AppSettings in the ScriptAddin.xll.config file.dir: the path where below files (scripts, args, results and diagrams) are stored.scriptorskipscript: full path of an executable script. In case the parameter isskipscriptthen the script execution is skipped (set this dynamically to prevent scripts from running).arg(input objects, by default these are .txt files): range name and path/filename, where the (input) arguments are stored.res/rres(output objects, by default these are .txt files): range name and path/filename, where the (output) results are expected. If the definition type is rres, results are removed from excel before saving and rerunning the scriptdiag(output diagrams, should be png format): range name and path/filename, where (output) diagrams are expected.scriptrng/scriptcellorskipscript(Scripts directly within Excel): either ranges, where a script is stored (scriptrng) or directly as a cell value (text content or formula result) in the 2nd column (scriptcell). In case the parameter isskipscriptthen the script execution is skipped (set this dynamically to prevent scripts from running).
Scripts (defined with the script, scriptrng or scriptcell definition types) are executed in sequence of their appearance. Although exec, path and dir definitions can appear more than once, only the last definition is used.
Instead of script, scriptrng and scriptcell there can also be given skipscript as the type, indicating that this script should be skipped in the current run. Typically you would define this dynamically via a function in excel, depending on some other setting.
In the 2nd column are the definition values as described above.
- For
arg,res,scriptrnganddiagthese are range names referring to the respective ranges to be taken as arg, res, scriptrng or diag target in the excel workbook. - The range names that are referred in
arg,res,scriptrnganddiagtypes can also be either workbook global (having no ! in front of the name) or worksheet local (having the worksheet name + ! in front of the name). They act at the same time as the filename for the input/output arguments and diagram files. So they can also contain extensions, in this case, the default extension.txtis not added. However for diag files, the content always has to be png format. - for
execthis can either be the full path for the executable, or - in case the executable is already in the windows default path - a simple filename (like cmd.exe or perl.exe). This overrides the standard settingExePath<ScriptType>. - for
typeany ScriptType available in the dropdown “ScriptExecutable”. This overrides the selection in the dropdown “ScriptExecutable”. - for
path, an additional path to folders with dlls/executables (semicolon separated), in case you need to add them. This overrides the standard settingPathAdd<ScriptType>. - for
envvar, the name of the environment variable to be added. This overrides the potential standard settingEnvironVarName<ScriptType>/EnvironVarValue<ScriptType>. - for
dira path that overrides the current workbook folder.
In the 3rd column are the definition paths of the files referred to in arg, res and diag
- Absolute Paths in dir or the definition path column are defined by starting with \ or X:\ (X being a mapped drive letter)
- parent folders for
arg,res,scriptrng/scriptcellanddiagentries. Not existing folders are created automatically, so dynamical paths can be given here. - for
exec, additional commandline switches can be passed here to the executable (like “/c” for cmd.exe, this is required to start a subsequent script). This overrides the standard settingExeArgs<ScriptType> - for
path, the default file suffix for the script files can be given here (“.R”, “.pl”, “.py”…). This overrides the standard settingFSuffix<ScriptType>. - for
envvar, the value of the environment variable to be added. - for
typea value ofnorno(case insensitive) can be used to disregard any output to standard err by the script engine as an error. This overrides the standard settingStdErrX<ScriptType>
The definitions are loaded into the ScriptDefinition dropdown either on opening/activating a Workbook with above named areas or by pressing the small dialogBoxLauncher “Show AboutBox” on the Script Addin Ribbon Tab and clicking “refresh ScriptDefinitions”:
The mentioned hyperlink to the local help file can be configured in the app config file (ScriptAddin.xll.config) with key “LocalHelp”. When saving the Workbook the input arguments (definition with arg) defined in the currently selected Scriptdefinition dropdown are stored as well. If nothing is selected, the first Scriptdefinition of the dropdown is chosen.
The error messages are logged to a diagnostic log provided by ExcelDna, which can be accessed by clicking on “show Log”. The log level can be set in the system.diagnostics section of the app-config file (Scriptaddin.xll.config):
Either you set the switchValue attribute of the source element to prevent any trace messages being generated at all, or you set the initializeData attribute of the added LogDisplay listener to prevent the generated messages to be shown (below the chosen level)
You can also run ScriptAddin in an automated way, simply issue the VBA command result = Application.Run("executeScript", <ScriptDefinitionName>, <headlessFlag>), where <ScriptDefinitionName> is the Name of the Script Definition Range and <headlessFlag> is a boolean flag indicating whether any user-interaction (as controllable by the Addin) should be avoided, all errors are returned in the result of the call.
Known Issues/Enhancements:
- Output redirected to the script output window is usually block buffered, so for more interactivity enable any buffer flushing (e.g. in Perl done with
$| = 1;). Buffer flushing however only works if newlines are printed, so output is still not seen until\n! - Input in the script output window is returning ALL key char values, so
my $val = <STDIN>;with user input ofa<Backspace key pressed>bwill yielda<BkSpc>bin$valinstead ofb. - Implement a faster way to save textfiles from excel
Installation of ScriptAddin and Settings
run Distribution/deployAddin.cmd (this puts ScriptAddin32.xll/ScriptAddin64.xll as ScriptAddin.xll and ScriptAddin.xll.config into %appdata%\Microsoft\AddIns and starts installAddinInExcel.vbs (setting AddIns(“ScriptAddin.xll”).Installed = True in Excel)).
Adapt the settings in ScriptAddin.xll.config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<section name="UserSettings" type="System.Configuration.NameValueSectionHandler"/>
</configSections>
<UserSettings configSource="ScriptAddinUser.config"/> : This is a redirection to a user specific config file containing the <appSettings> ... </appSettings> information below (in the same path as ScriptAddin.xll.config). These settings always override the central appSettings
<appSettings file="\\Path\to\ScriptAddinCentral.config"> : This is a redirection to a central config file containing the <appSettings> ... </appSettings> information below (any path). The central config file overrides the settings below.
<add key="ExePathR" value="C:\Program Files\R\R-4.0.4\bin\x64\Rscript.exe" /> : The Executable Path used for R
<add key="FSuffixR" value=".R" /> : The File suffix used when writing temporary Files used in scriptrng/scriptcell for R
<add key="StdErrXR" value="False" /> : Shall any output to standard err by R be regarded as an error that blocks further processing (default: True)
<add key="ExePathPerl" value="C:\Strawberry\perl\bin\perl.exe" />
<add key="PathAddPerl" value="C:\Strawberry\c\bin;C:\Strawberry\perl\site\bin;C:\Strawberry\perl\bin" /> : Additional Path Setting for Perl
<add key="FSuffixPerl" value=".pl" />
<add key="EnvironVarNamePerl" value="PERL5LIB" />
<add key="EnvironVarValuePerl" value="C:\Users\rolan\specialLib" />
<add key="ExePathPython" value="C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\pythonw.exe" />
<add key="PathAddPython" value="C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\Scripts;C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\Library\bin;C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\Library\bin;C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\Library\usr\bin;C:\Users\rolan\anaconda3\Library\mingw-w64\bin" />
<add key="FSuffixPython" value=".py" />
<add key="ExePathWinCmd" value="C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" />
<add key="ExeArgsWinCmd" value="/C" /> : Any additional arguments to the script executable
<add key="FSuffixWinCmd" value=".cmd" />
<add key="ExePathCscript" value="C:\Windows\System32\cscript.exe" />
<add key="FSuffixCscript" value=".js" />
<add key="presetSheetButtonsCount" value="24"/> : the preset maximum Button Count for Sheets (if you expect more sheets with ScriptDefinitions, you can set it accordingly)
<add key="DebugAddin" value="True"/> : activate Info messages in Log Display to debug addin.
<add key="disableSettingsDisplay" value="addin"/> : enter a name here for settings that should not be available for viewing/editing to the user (addin: ScriptAddin.xll.config, central: ScriptAddinCentral.config, user: ScriptAddinUser.config).
<add key="LocalHelp" value="\\LocalPath\to\LocalHelp.htm" /> : If you download this page to your local site, put it there to have it offline.
<add key="localUpdateFolder" value="" /> : For updating the Script-Addin Version, you can provide an alternative folder, where the deploy script and the files are maintained for other users.
<add key="localUpdateMessage" value="New version available in local update folder, start deployAddin.cmd to install it:" /> : For the alternative folder update, you can also provide an alternative message to display.
<add key="updatesDownloadFolder" value="C:\temp\" /> : You can specify a different download folder here instead of C:\temp\.
<add key="updatesMajorVersion" value="1.0.0." /> : Usually the versions are numbered 1.0.0.x, in case this is different, the Major Version can be overridden here.
<add key="updatesUrlBase" value="https://github.com/rkapl123/DBAddin/archive/refs/tags/" /> : Here, the URL base for the update zip packages can be overridden.
</appSettings>
<system.diagnostics>
<sources>
<source name="ExcelDna.Integration" switchValue="All">
<listeners>
<remove name="System.Diagnostics.DefaultTraceListener" />
<add name="LogDisplay" type="ExcelDna.Logging.LogDisplayTraceListener,ExcelDna.Integration">
<!-- EventTypeFilter takes a SourceLevel as the initializeData:
Off, Critical, Error, Warning (default), Information, Verbose, All -->
<filter type="System.Diagnostics.EventTypeFilter" initializeData="Warning" />
</add>
</listeners>
</source>
</sources>
</system.diagnostics>
</configuration>
In the ScriptAddinUser.config setting file, there are two settings that are persisted by the addin itself, so they should not really be changed:
<appSettings>
<add key="debugScript" value="True"/> : whether the script output is active or inactive
<add key="selectedScriptExecutable" value="0"/> : the currently selected executable for script execution (with dropdown ScriptExecutable)
</appSettings>
The settings for the scripting executables are structured as follows <ScriptExecPrefix><ScriptType> and form the selection of available script types in ScriptAddin.
Following ScriptExecPrefixes are possible:
- ExePath: The Executable Path used for the ScriptType
- EnvironVarName: An environment variable name to be added for all processes of ScriptType
- EnvironVarValue: The value of the above environment variable
- PathAdd : Additional Path Setting for the ScriptType
- FSuffix : The File suffix used when writing temporary Files used in scriptrng/scriptcell (Scripts directly within Excel), sometimes important to the script engine (e.g. cscript makes a difference between .vbs and .js)
- StdErrX : Shall any output to standard error by the ScriptType engine be regarded as an error that blocks further processing (default: True)
- ExeArgs : Any additional arguments to the ScriptType executable
The minimum requirement for a scripting engine to be regarded as selectable/usable is the ExePath entry. All other ScriptExecPrefixes are optional depending on the requirement of the scripting engine.
There are three settings files which can be used to create a central setting repository (<appSettings file="your.Central.Configfile.Path">) along with a user specific overriding mechanism (<UserSettings configSource="ScriptAddinUser.config"/>) defined in the application config file ScriptAddin.xll.config. All three settings files can be accessed in the ribbon bar beneaht the dropdown Settings.
Additionally you can find an insert Example mechanism in this dropdown that adds an example script definition range with the above described definition types and example configs.
Building
All packages necessary for building are contained, simply open ScriptAddin.sln and build the solution. The script deployForTest.cmd can be used to deploy the built xll and config to %appdata%\Microsoft\AddIns